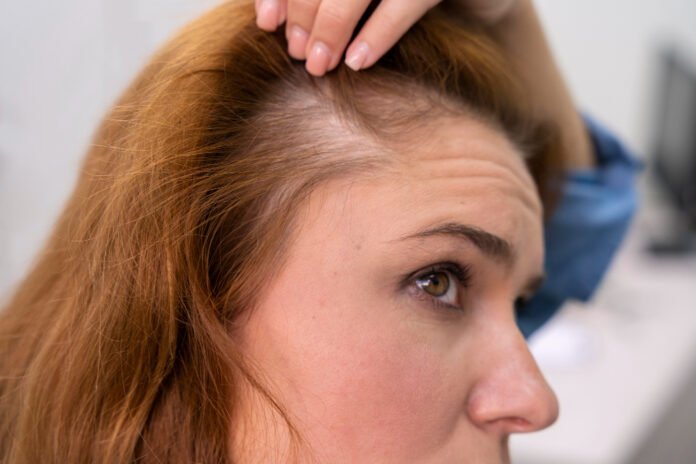
Notice more hair in your brush than usual? Does your part seem a little wider? If you’re in your 20s or 30s, discovering thinning hair can be a concerning experience. You might wonder if it’s normal to experience hair loss at such a young age. The short answer is yes, it’s surprisingly common. While often associated with older age, a significant number of young adults experience hair thinning. This isn’t just a cosmetic concern; it can be a source of considerable stress and anxiety.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through why you might be experiencing premature hair loss, whether it’s a normal phenomenon, and what you can do about it.
The Numbers Don’t Lie: Hair Loss in Young Adults is Common

Statistics show that a noticeable percentage of both men and women experience hair loss in their 20s and 30s. For many, this is the beginning of androgenetic alopecia, more commonly known as male or female pattern baldness. Studies reveal that by the age of 30, roughly 25-30% of men will have some degree of hair loss. While less documented for women, the incidence of thinning hair in the 20s and 30s is also on the rise.
So, if you’re seeing signs of hair loss, you’re far from alone. While it may be a “normal” occurrence from a statistical standpoint, it’s essential to understand the underlying causes to address it effectively.
Unpacking the Causes: Why is Your Hair Thinning?
Several factors can contribute to premature hair loss. Identifying the root cause is the first step toward finding a solution.
Genetics: The Most Common Culprit

The leading cause of hair loss in both men and women is androgenetic alopecia. This is a hereditary condition, meaning it’s passed down through your family’s genes. If your parents or grandparents experienced hair loss, you have a higher likelihood of experiencing it too.
- For men, androgenetic alopecia typically presents as a receding hairline and thinning at the crown, often referred to as male pattern baldness.
- For women, it usually manifests as a diffuse thinning all over the scalp, with the part line often becoming more pronounced. This is known as female pattern hair loss.
This genetic predisposition makes hair follicles more sensitive to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. DHT can shrink hair follicles, leading to shorter, finer hairs and eventually stopping hair growth altogether.
Telogen Effluvium: The Stress Shed

Have you recently gone through a significant life event, a period of high stress, a major illness, or a dramatic weight change? You might be experiencing telogen effluvium. This is a temporary form of hair loss where a large number of hair follicles prematurely enter the shedding (telogen) phase of the hair growth cycle. This results in a sudden and often diffuse shedding of hair a few months after the triggering event. The good news is that this type of hair loss is usually reversible once the stressor is removed.
Hormonal Imbalances: A Key Factor for Women
Fluctuations in hormone levels can significantly impact hair growth. For women in their 20s and 30s, several conditions can lead to hormonal imbalances that cause hair thinning:

- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This endocrine disorder is a common cause of hair loss in young women. PCOS can lead to an overproduction of androgens, contributing to the same type of hair thinning seen in androgenetic alopecia.
- Thyroid Problems: Both an overactive (hyperthyroidism) and underactive (hypothyroidism) thyroid can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to diffuse hair loss.
- Pregnancy and Postpartum: The hormonal shifts during and after pregnancy can cause changes in hair. Many women experience thicker hair during pregnancy, followed by a period of shedding (postpartum telogen effluvium) a few months after giving birth.
Nutritional Deficiencies: Fueling Your Follicles
Your hair needs a steady supply of vitamins and minerals to grow strong and healthy. A poor diet or certain health conditions that affect nutrient absorption can lead to hair loss. Key nutrients for hair health include:

- Iron: Iron deficiency (anemia) is a well-known cause of hair loss, particularly in women.
- Zinc: This mineral plays a crucial role in hair tissue growth and repair.
- Vitamins D, B12, and Biotin: Deficiencies in these vitamins have been linked to hair thinning.
Lifestyle and Styling Habits
Certain lifestyle choices and hairstyling practices can also contribute to hair loss:

- Traction Alopecia: Constantly pulling your hair into tight hairstyles like ponytails, braids, or buns can cause gradual hair loss from the tension.
- Harsh Treatments: Frequent use of harsh chemical treatments, such as bleaching and straightening, can damage the hair shaft and lead to breakage and thinning.
Taking Control: Solutions and Treatments for Hair Loss
The good news is that many types of hair loss can be treated or managed, especially when addressed early. Here are some steps you can take:
Consult a Professional

The first and most crucial step is to get an accurate diagnosis. A dermatologist or a trichologist (a hair and scalp specialist) can help identify the cause of your hair loss through a physical examination, blood tests, and a review of your medical and family history.
Medical Treatments
Based on your diagnosis, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following treatments:

- Minoxidil (Rogaine®): This over-the-counter topical treatment is FDA-approved for both men and women and can help stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss.
- Finasteride (Propecia®): This prescription oral medication for men works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT. It is not typically prescribed for women of childbearing age.
- Spironolactone: For women with hair loss due to high androgen levels (like in PCOS), this prescription medication can be effective.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: This involves injecting your concentrated platelets into the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes

Eat a Balanced Diet: Ensure your diet is rich in lean protein, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Pay special attention to iron, zinc, and vitamin D intake. Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine, such as exercise, yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. Gentle Hair Care: Be kind to your hair. Use a gentle shampoo, avoid tight hairstyles, and limit the use of heat styling and harsh chemical treatments. Consider Supplements: If a nutritional deficiency is identified, your doctor may recommend specific supplements. However, it’s important not to self-prescribe, as excessive amounts of certain vitamins can also be harmful.
The Bottom Line: Early Action is Key
While experiencing hair loss in your 20s and 30s can be distressing, it’s a common issue with a variety of potential causes and effective solutions. The most important takeaway is to address it early. Don’t wait for the thinning to become severe. By seeking professional advice and taking proactive steps, you can often slow down the progression of hair loss and, in many cases, even encourage regrowth. Remember, a healthy scalp is the foundation for healthy hair.